What is an Endometrial Biopsy?
Endometrial Biopsy
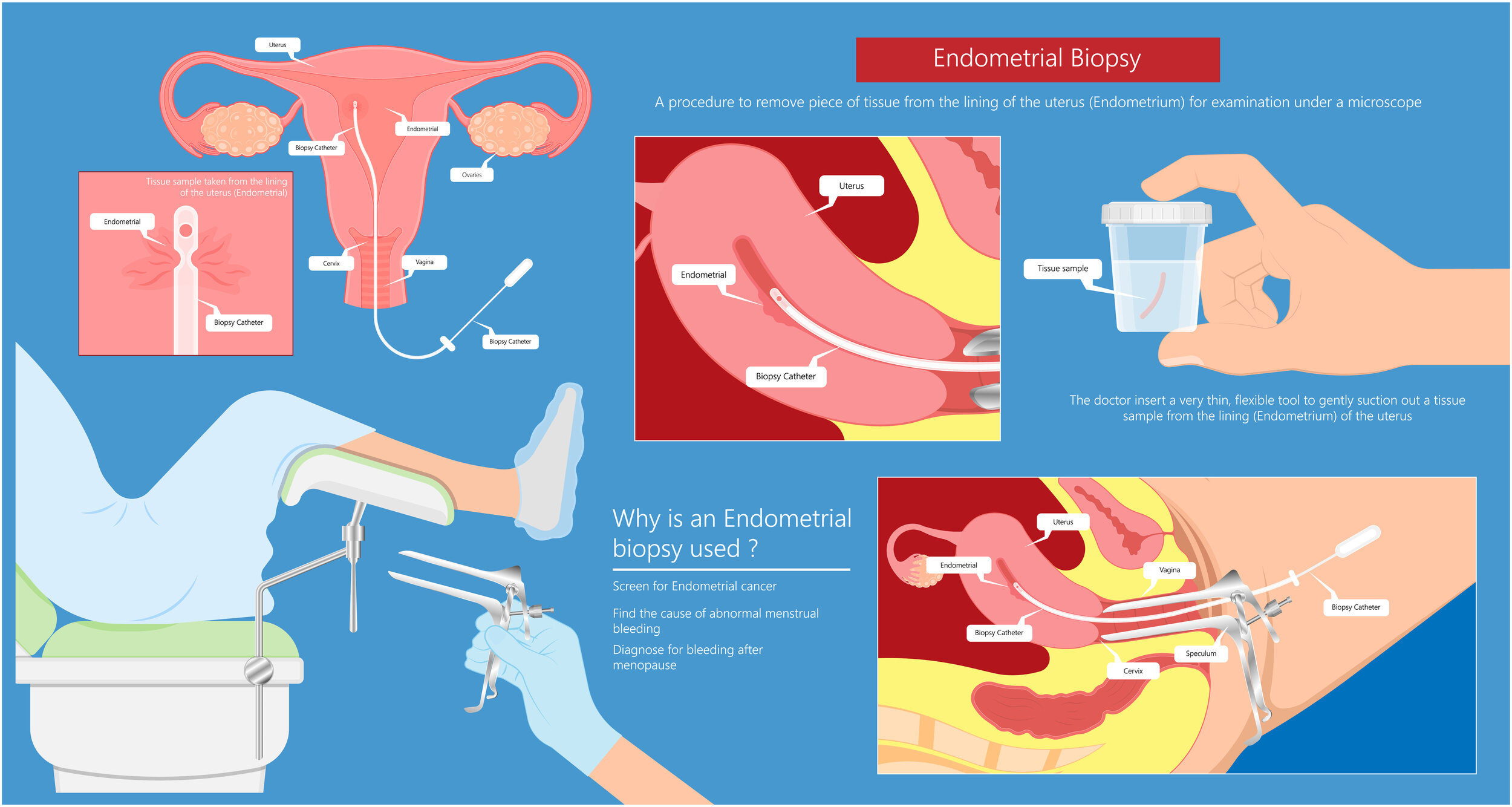
An endometrial biopsy is a medical procedure in which a small piece of tissue from the lining of the uterus (the endometrium) is removed for examination under a microscope. The removed tissue is examined for cancer or any other cell abnormalities. It is done to diagnose bleeding problems. The procedure is often done in a doctor’s office.
Why is an endometrial biopsy done?
An endometrial biopsy is done to help your doctor find out the cause of problems leading to heavy or irregular bleeding. It is the most common test done to diagnose endometrial cancer. Though it is a simple office procedure, it needs to be performed by a provider who has experience in performing the test. The biopsy also lets your doctor check to see if your body's endometrial hormone levels are balanced.
Who might need an endometrial biopsy?
Endometrial biopsies are typically done on women over the age of 35 and prior to menopause. It cannot be done on pregnant women. Sometimes a biopsy will be done on a woman who is having trouble getting pregnant to see if the infertility is linked to a problem with the endometrium.
What symptoms might suggest you need an endometrial biopsy?
If you have any of the following, your provider may recommend an endometrial biopsy:
Heavy or very long menstrual periods
Irregular menstruation
Bleeding after menopause
Abnormal bleeding in women taking tamoxifen, a breast cancer medicine
Thickened uterine lining, determined by an ultrasound
How is an endometrial biopsy done?
An endometrial biopsy is usually done in your doctor’s office. It is most often done without anesthesia. You will be placed with your feet in stirrups.
Your doctor will insert a speculum into the vagina to hold it open so that your cervix can be viewed (similar to a Pap test). Your cervix will then be cleaned with a special solution. Another instrument may be used to hold the cervix steady, while a very thin suction tube is inserted into the uterus to collect the tissue sample. The tissue will then be sent to a pathologist for analysis of the cells.
You will be advised not to use tampons, douche, or have intercourse in the days after your test. Some providers may also ask that you avoid swimming, going in a hot tub, or taking baths for about a week after the procedure. Your doctor will review the exact instructions with you after the procedure.
You may experience cramping similar to menstrual cramps during and after the procedure. You may be prescribed an over the counter pain reliever such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen to deal with the pain.
The whole procedure will usually take between 5 and 15 minutes.
What are the benefits of an endometrial biopsy?
An endometrial biopsy is the most common and accurate test used to diagnose endometrial cancer. The lab should have the results in about a week. Your physician will share the results with you and go over a treatment plan depending on the results.